Customer story
Producing long-term renewable power from IKEA’s wood residue

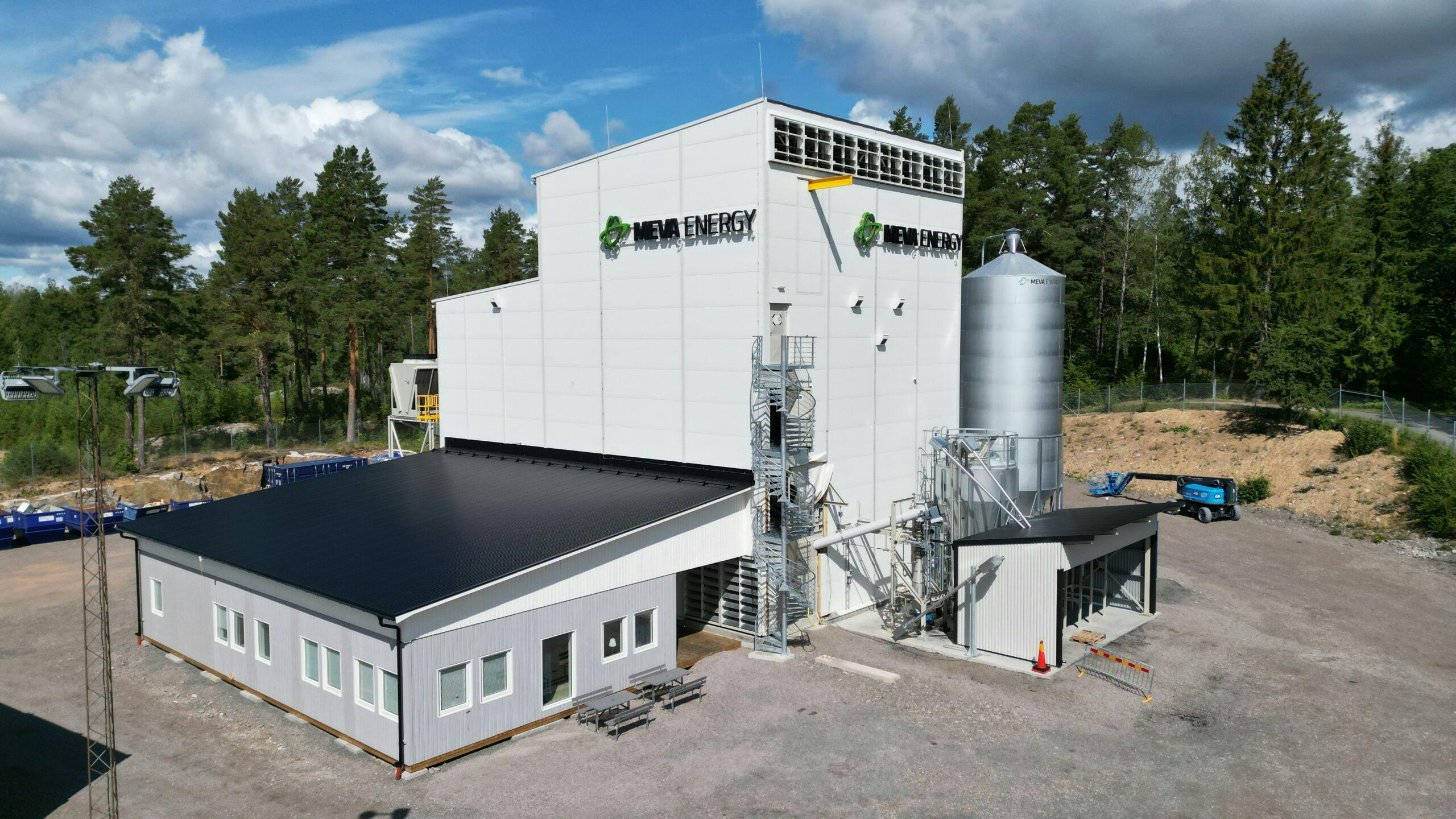
IKEA Industry uses MEVA Energy’s co-generation power plant to cut emissions
At the IKEA Industry plant, power and heat consumption are the largest sources of CO2 emissions. Learn how the company is collaborating with our portfolio start-up, MEVA Energy – a game-changing co-generation power plant – to substantially cut its carbon footprint by 2025.


The challenge
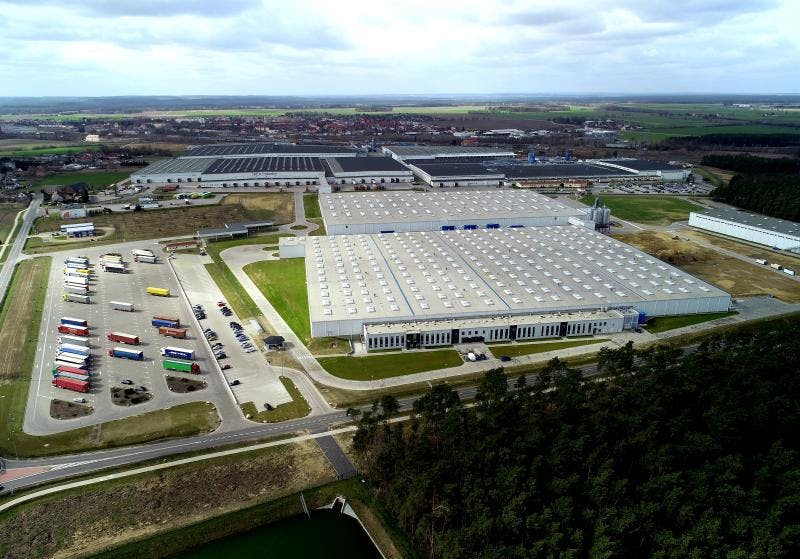
IKEA Industry’s largest manufacturing unit, located in Zbaszynek, Poland, produces wooden furniture for IKEA. Power and heat consumption represent the plant’s most significant sources of CO2 emissions. The company has set an ambitious target: to reduce its carbon footprint by 80% by 2025 as compared to the level recorded in 2016. A key step towards achieving this goal is utilising renewable power across its manufacturing plants.
The solution
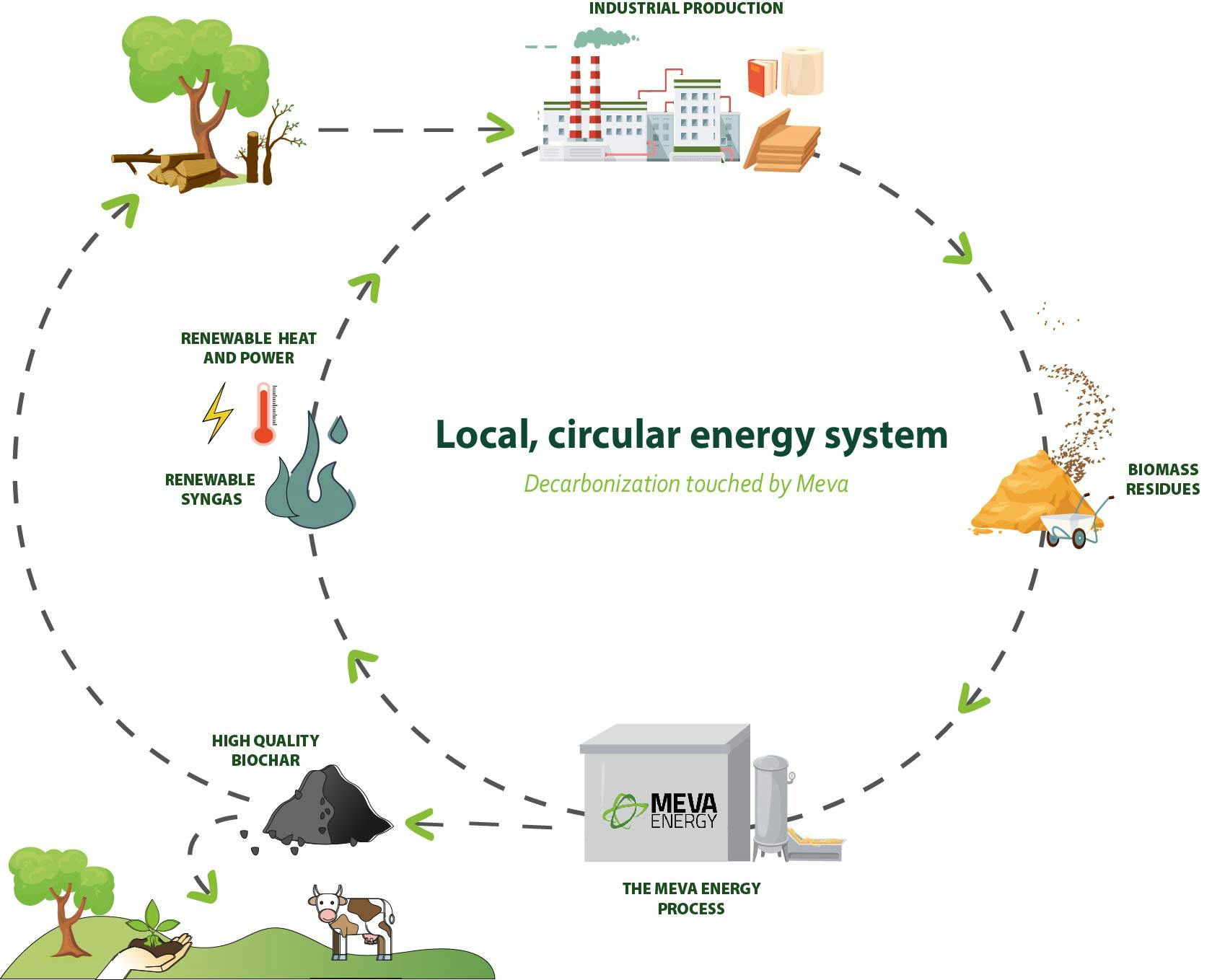
This is where MEVA Energy comes in – a turn-key power plant for co-generated production of power and heat from biomass feedstock. The solution operates at a level that surpasses the current commercial feasibility of steam turbine technology.
For IKEA Industry, MEVA Energy’s thermochemical conversion technology provides a way to use the plant’s vast quantities of low value feedstock (wood residue), transforming it into high-efficiency renewable power production:
- 2.8 MW power station to be fueled by renewable gas obtained from wood residue feedstock.
- 19 GWh produced every year.
- 10-year contract whereby MEVA Energy delivers and sells power and wood residue reception services to IKEA Industry.
- 16,000 tons of waste wood, contaminated with glue, up-cycled to renewable energy per year

The expected impact
The expected benefits for IKEA Industry are:
- Up to 20,000 tons CO2 reduction per year
- 2,8 MW renewable power from wood residue feedstock.
- Wood residue transportation savings: 300 truck journeys per year
- Fully circular and decentralised energy system created on-site
- Reduction in air pollution compared with previous wood combustion methods.